
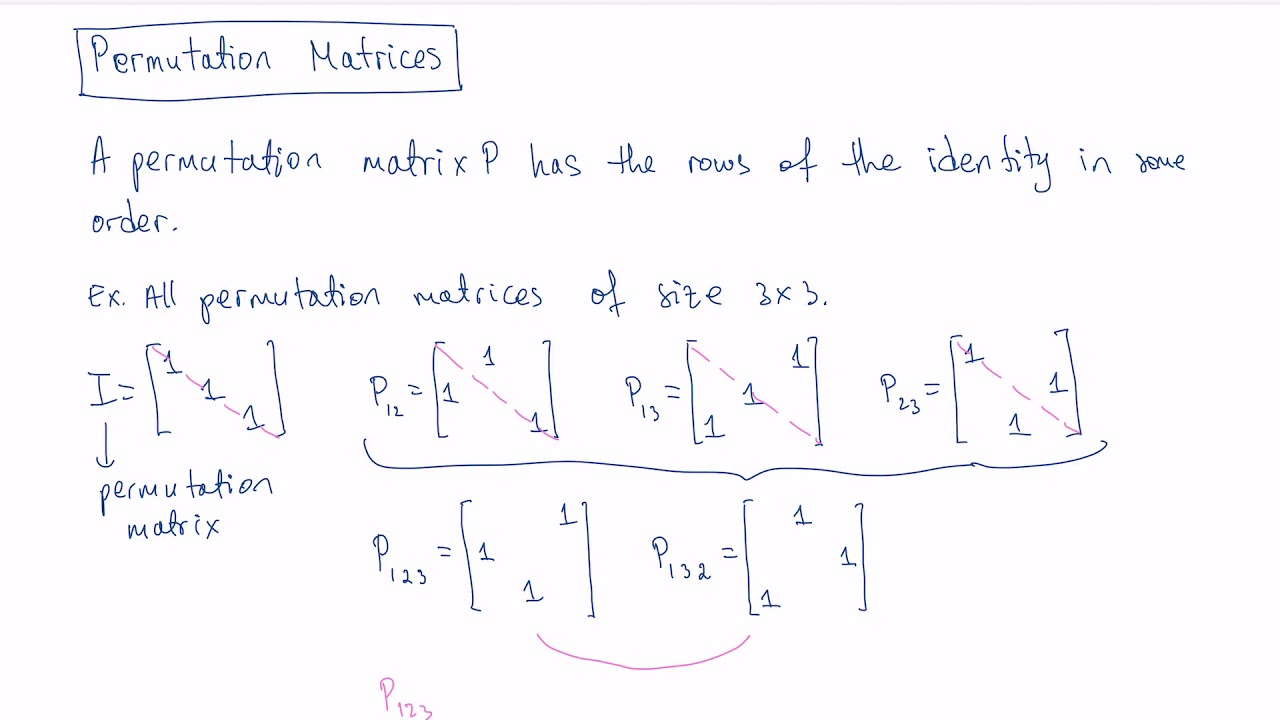
Where and are square, nonempty submatrices. Recall that a matrix is irreducible if there does not exist a permutation matrix such that The shift matrix plays a fundamental role in characterizing irreducible permutation matrices. The following animated gif superposes MATLAB spy plots of, , …. The matrix has two diagonals of s, which move up through the matrix as it is powered: for and. It is easy to show that, which means that the eigenvalues of are, where is the th root of unity. A general permutation matrix can be written as a product of elementary permutation matrices, where is such that. Such a matrix is symmetric and so satisfies, and it has determinant. It can be written, where is the th column of. Note that is a symmetric Hankel matrix and is a circulant matrix.Īn elementary permutation matrix differs from in just two rows and columns, and, say. Pre- or postmultiplying a matrix by shifts the rows or columns, respectively, one place forward and moves the first one to the last position-that is, it cyclically permutes the rows or columns. Pre- or postmultiplying a matrix by reverses the order of the rows and columns, respectively. A permutation matrix that has the desired reordering effect is constructed by doing the same operations on the identity matrix.Įxamples of permutation matrices are the identity matrix, the reverse identity matrix, and the shift matrix (also called the cyclic permutation matrix), illustrated for by Premultiplying a matrix by reorders the rows and postmultiplying by reorders the columns. The total number of permutation matrices is. Such a matrix, say, is orthogonal, that is,, so it is nonsingular and has determinant. A permutation matrix is a square matrix in which every row and every column contains a single and all the other elements are zero.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
